Theory X and Theory Y
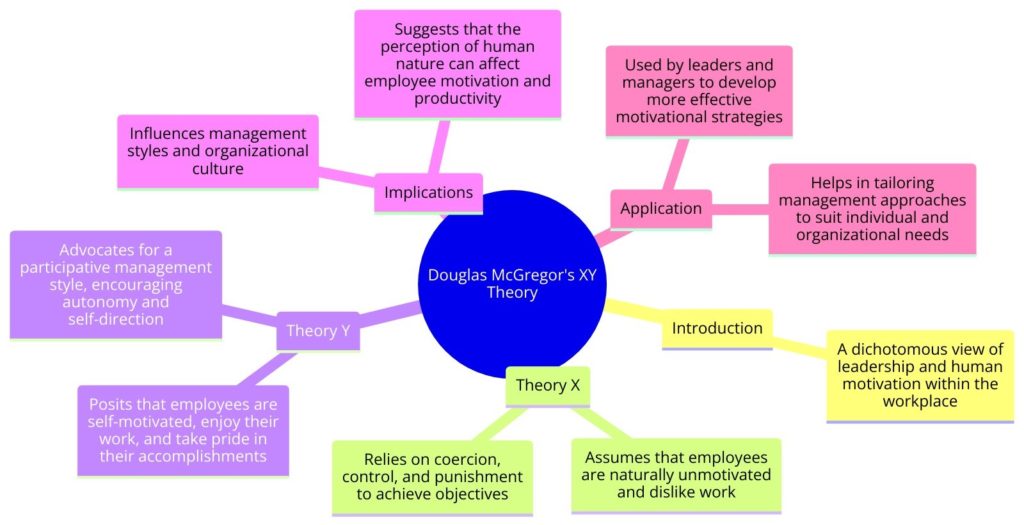
Douglas McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y, collectively known as the XY Theory, represent a dichotomous view of leadership and human motivation within the workplace. Introduced in McGregor’s 1960 book, “The Human Side of Enterprise,” these theories challenge managers to assess their underlying beliefs about their employees’ motivations, which in turn influences their management style. McGregor posited that a manager’s perception of the nature of human beings is based on a certain grouping of assumptions and that these assumptions mold the manager’s behavior toward the employees.
What is McGregor’s XY Theory?
Theory X and Theory Y offer contrasting models of workforce motivation and have been used to derive different management styles.
- Theory X assumes that employees are inherently lazy, need constant supervision, and are motivated primarily by financial rewards. According to this view, people work only when they are forced or incentivized with money, and they prefer to be directed to avoid responsibility. Therefore, a Theory X manager tends to be more authoritarian, preferring a top-down approach to management that emphasizes control and coercion.
- Theory Y, on the other hand, offers a more positive view. It suggests that employees are self-motivated, seek out responsibility, and find intrinsic value in their work. People under Theory Y are considered capable of self-direction and self-control and can be trusted to achieve the objectives to which they are committed. A Theory Y manager believes in the potential of employees to exhibit high levels of creativity and innovation when given the chance. This management style is more participative, involving employees in decision-making and encouraging a more collaborative work environment.
Why It Is Valuable
McGregor’s XY Theory is valuable for several reasons:
- Cultural Insight: It provides insights into how the underlying beliefs of managers about human nature can shape organizational culture and employee relations.
- Management Styles: By understanding the implications of Theory X and Theory Y, leaders can better assess their management style and its impact on motivation, engagement, and productivity.
- Employee Motivation: The theory highlights the significance of intrinsic motivation, suggesting that recognizing and nurturing employees’ self-motivation and responsibility can lead to higher satisfaction and performance.
- Adaptability: It encourages managers to adopt a more flexible management style, tailoring their approach to the needs and capabilities of their team members.
When and How to Use It
McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y can be applied in various organizational contexts, including leadership development, team management, HR practices, and organizational culture transformation. Leaders and managers can use these theories to:
- Reflect on and potentially modify their assumptions about employee motivation.
- Design management and motivational strategies that align more closely with the Theory Y perspective to encourage greater engagement and innovation.
- Foster a culture that values autonomy, responsibility, and participative decision-making.
Shortcomings/Criticisms
Despite its widespread influence, McGregor’s XY Theory has faced several criticisms:
- Oversimplification: The binary nature of Theory X and Theory Y has been criticized for oversimplifying the complex spectrum of human behavior and motivation.
- Cultural Bias: Some argue that the theories, particularly Theory Y, may reflect a cultural bias, assuming conditions that favor Western, particularly American, workplace values and attitudes.
- Practical Application: Implementing a Theory Y management style can be challenging in practice, especially in traditional, hierarchical organizations or in industries where routine tasks predominate.
- Evolution of Work: The changing nature of work, particularly with advances in technology and the rise of remote and flexible working arrangements, may require a more nuanced approach than what is offered by the binary classification of Theory X and Theory Y.
Douglas McGregor’s XY Theory has had a profound impact on management theory and practice by challenging leaders to examine their assumptions about employee motivation and to consider more humane and effective approaches to management. While it may have limitations in its application, the fundamental insights it provides into human motivation and organizational behavior remain relevant, encouraging a more adaptive, inclusive, and participative approach to leadership.