Hello, this page’s contents are restricted and exclusive to our members. To view or personalize and use, please Log in. If you are not a member, please Subscribe to one of our affordable plans. Please support our site to help us provide quality content consistently. See our Pricing plan If you are not ready for a paid membership, consider our basic Free Plan.
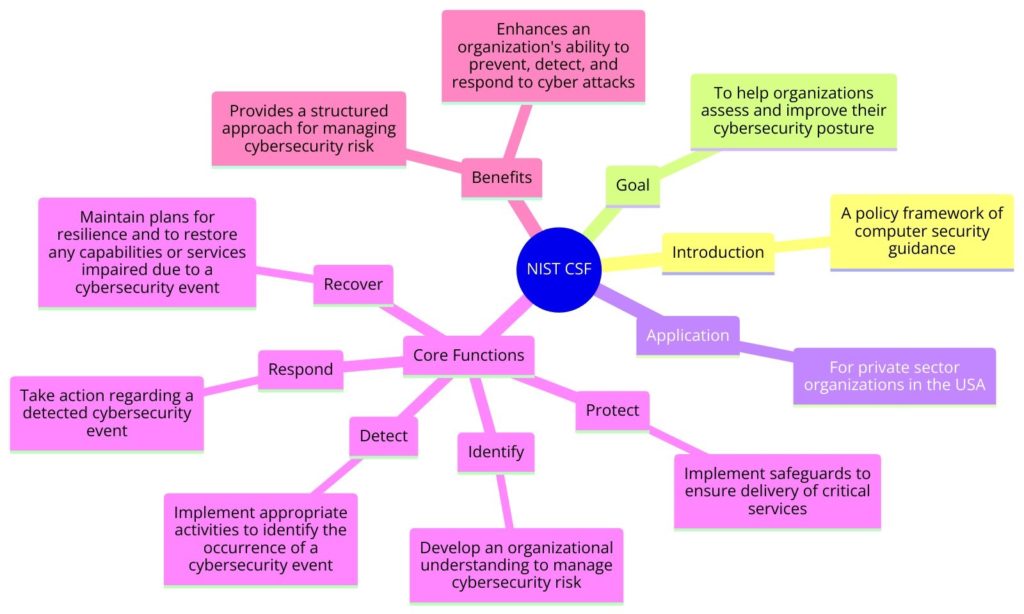
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
By A Staff Writer | Updated 28 Aug, 2024