Data Management Maturity Model
The Data Management Maturity (DMM) Model is a comprehensive framework designed to help organizations evaluate and improve their data management practices. Developed by the CMMI Institute, which is part of Carnegie Mellon University, the DMM Model provides a structured approach for organizations to assess their current data management capabilities, identify areas for improvement, and implement best practices in data management. The model is based on the principles of the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI), a process improvement training and appraisal program.
What is the DMM Model?
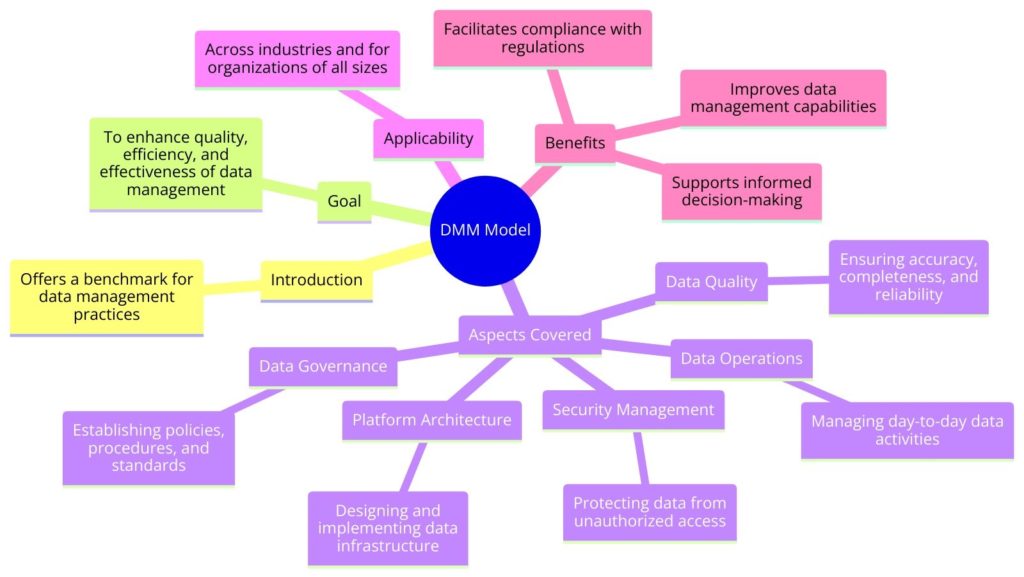
The DMM Model offers organizations a way to benchmark their data management practices against an established standard, with the goal of enhancing the quality, efficiency, and effectiveness of their data management processes. The model covers various aspects of data management, including data governance, data quality, data operations, platform architecture, and security management. It is designed to be applicable across industries and for organizations of all sizes.
Origin of the Framework
The Data Management Maturity Model was developed by the CMMI Institute to address the growing recognition of data as a critical asset for organizations. In an era where data-driven decision-making is key to competitive advantage, the need for a standardized framework to assess and improve data management capabilities became apparent. The DMM Model leverages the CMMI Institute’s expertise in developing maturity models to create a comprehensive guide for effective data management.
How It Works
The DMM Model assesses an organization’s data management practices across six Process Areas, each representing a core component of data management:
- Data Governance: Ensuring that data management activities are aligned with organizational goals and that data-related risks are managed appropriately.
- Data Quality Management: Establishing processes to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of data.
- Data Operations: Managing the operational aspects of data collection, storage, and maintenance.
- Platform and Architecture: Developing a sustainable and scalable infrastructure that supports data management needs.
- Project and Portfolio Management: Managing data-related projects and initiatives effectively.
- Security Management: Protecting data from unauthorized access and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
Organizations use the DMM Model to conduct self-assessments or engage with certified appraisers for formal assessments. The model identifies strengths and weaknesses in current practices and provides a roadmap for progressing through five levels of maturity, from Initial (Level 1) to Optimizing (Level 5).
Why It Is Valuable
The DMM Model provides several benefits to organizations looking to enhance their data management capabilities:
- Improves Data Quality: By adopting best practices in data management, organizations can improve the quality of their data, leading to better decision-making.
- Enhances Efficiency: Streamlining data management processes reduces operational inefficiencies and can significantly lower costs.
- Mitigates Risk: Effective data governance and security management reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
- Facilitates Growth: A strong data management foundation supports the organization’s growth and adaptation to changes in the business environment.
When and How to Use It
Organizations can use the DMM Model at any stage of their data management journey. It is particularly useful for organizations that:
- Recognize data as a strategic asset and want to leverage it more effectively.
- Are experiencing data-related challenges that impact business performance.
- Need to assess their data management practices against an industry standard.
- Are you preparing for or undergoing digital transformation initiatives?
Implementing improvements based on the DMM Model involves:
- Conducting a baseline assessment to determine the current maturity level.
- Identifying gaps and areas for improvement.
- Developing an action plan to address identified gaps.
- Implementing changes and monitoring progress.
- Reassessing maturity periodically to gauge improvement and identify new opportunities for enhancement.
Shortcomings/Criticisms
While the DMM Model is a powerful tool for improving data management practices, there are some criticisms:
- Resource Intensive: Small organizations may find the model challenging to implement due to the resources required for a comprehensive assessment and improvement process.
- Complexity: The comprehensive nature of the model can be daunting, and organizations may require external expertise to navigate the assessment and improvement process effectively.
- Flexibility: Some critics argue that the model may not be flexible enough to accommodate the unique needs and contexts of all organizations, particularly those in rapidly evolving industries.
The Data Management Maturity Model offers a structured approach for organizations to assess and improve their data management practices, leading to enhanced data quality, efficiency, and competitive advantage. While challenges exist in implementing the model, especially for smaller organizations, the benefits of improved data management are significant for any organization that relies on data as a critical asset.